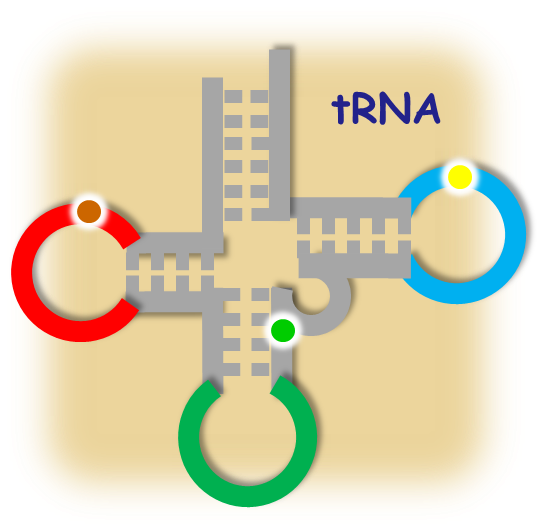
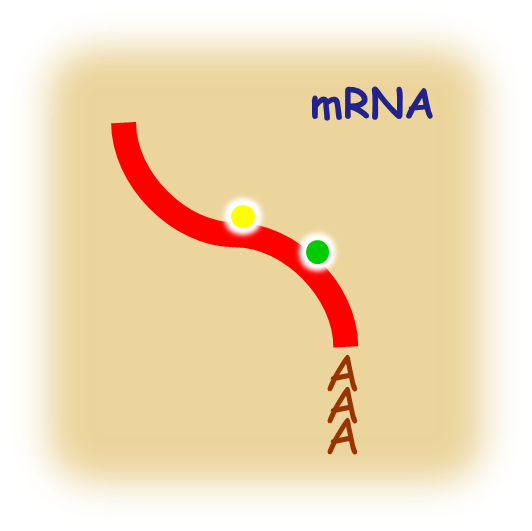
Triticum aestivum (bread wheat) is an important global cereal. Bread wheat is hexaploid, and its estimated genome is ~17 Gb. The ancestral progenitors are thought to be Triticum urartu (the A-genome donor) and a grass related to Aegilops speltoides (the B-genome donor). Their hybridization produced tetraploid wheat (AABB, T. dicoccoides), which further hybridized with Aegilops tauschii (the D-genome donor) to produce modern bread wheat. T. aestivum genome sequences are avaliable from Ensembl. The draft genome of T. urartu was published on Nature in 2013 (ref). |
Webmaster: Xuan Ma
College of Life Sciences,Tianjin Normal University,Tianjin, 300387, China