Plant tRNA & tRF Expression DB
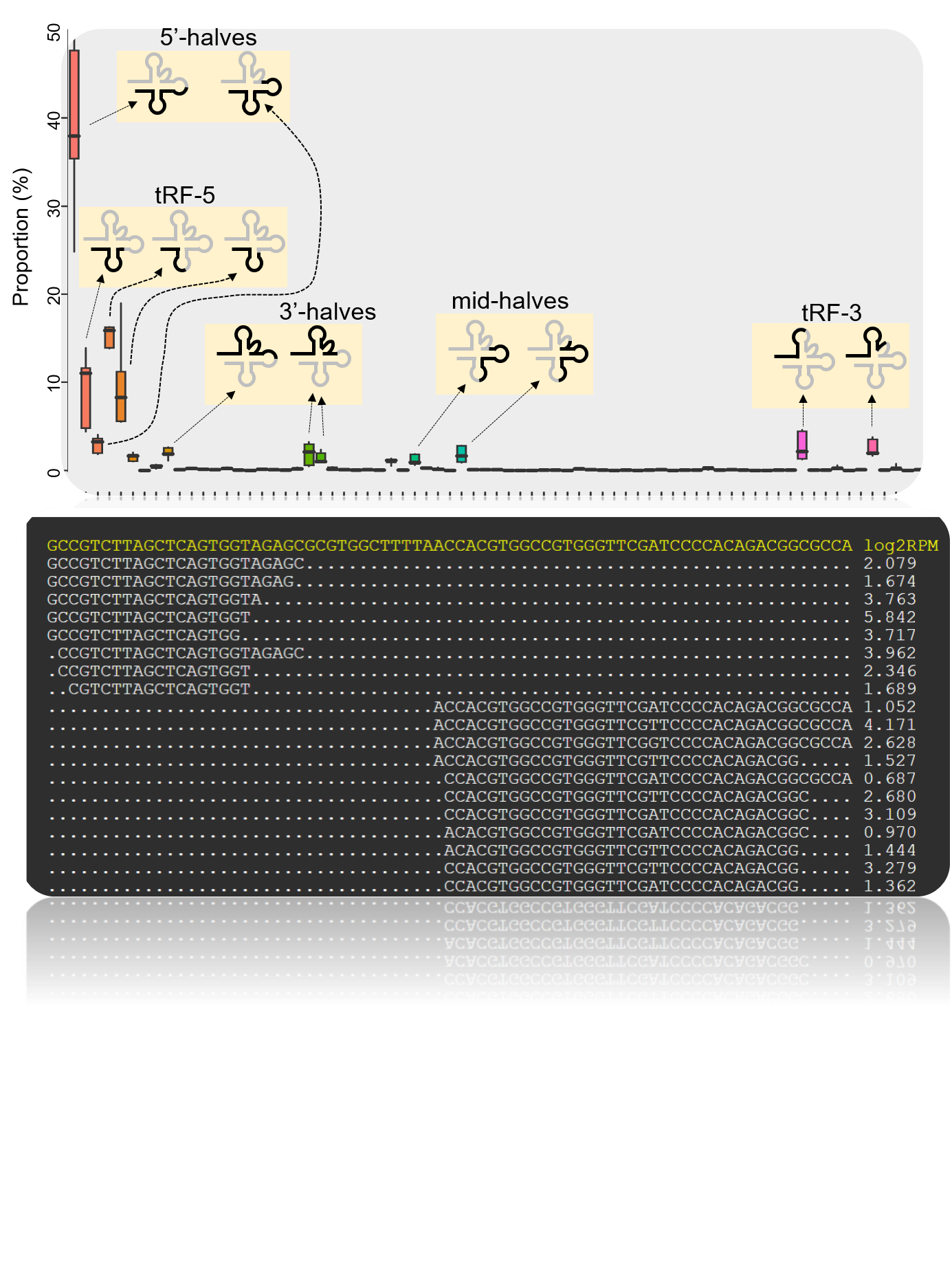
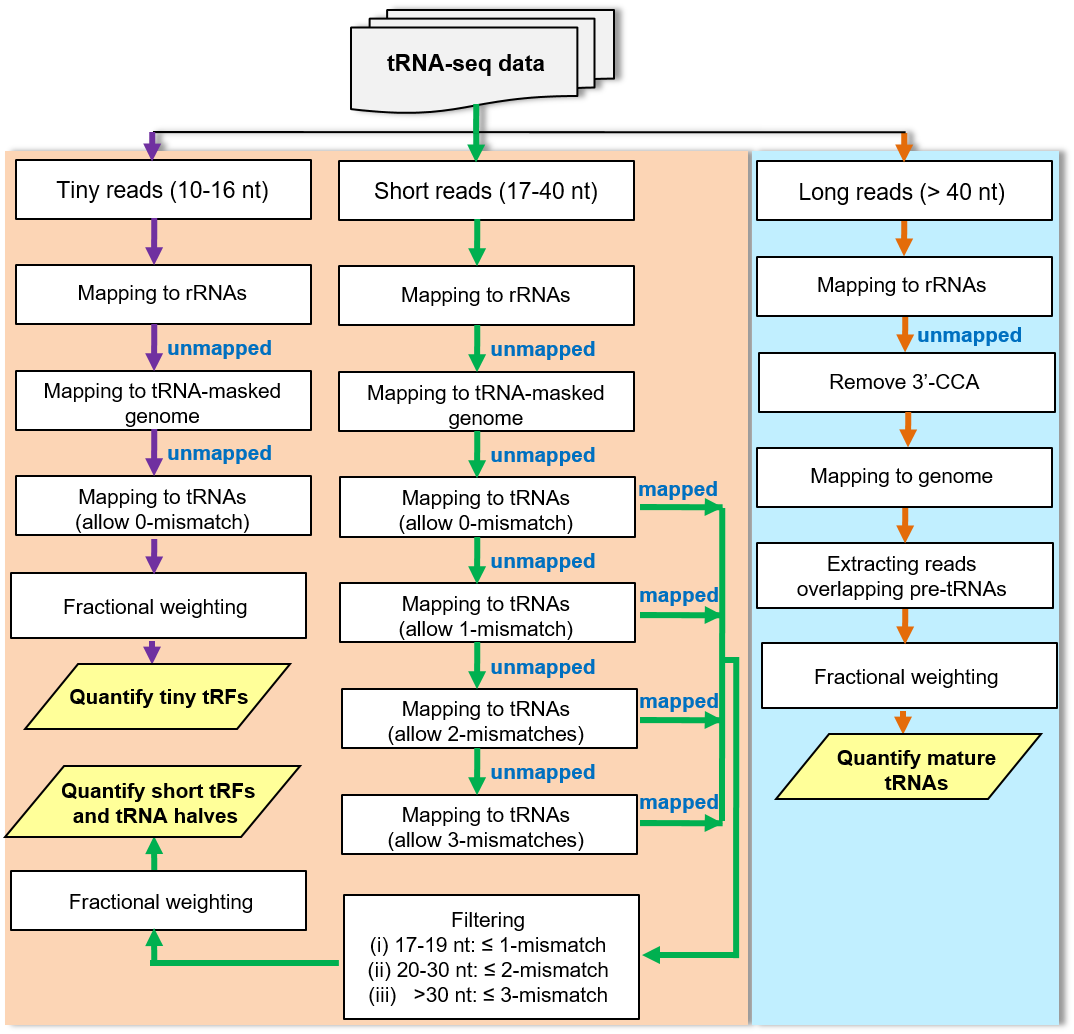
This web portal presents tRNA and tRF expression data obtained by tRNA-seq in the model plants Arabidopsis thaliana and Oryza sativa.
Citation: Ma X #*, Liu C*, Kong X, Liu J, Zhang S, Liang S, Luan W#, Cao X#. Sci China Life Sci., 2021 Feb 8.